Revised
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF.
See the companion publication N1112, Protein handout.
This poster highlights different protein choices, reviews nutrients and fat provided, and provides tips for making lean protein choices and incorporating a variety of protein foods into a healthy diet.
Topics
- Nutrition
- Health
- Protein
- Lean
- Nutrients
- Seafood
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Vegetarian
- SNAP
Pages
- One 24 x 36 inches poster
See poster content below.
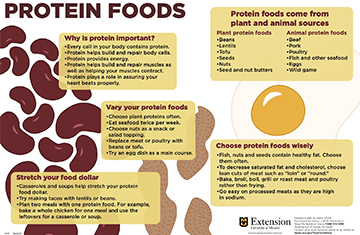
Protein Foods
Why is protein important?
- Every cell in your body contains protein.
- Protein helps build and repair body cells.
- Protein provides energy.
- Protein helps build and repair muscles as well as helping your muscles contract.
- Protein plays a role in ensuring your heart beats properly.
Protein foods come from plant and animal sources.
Plant protein foods
- Beans
- Lentils
- Tofu
- Seeds
- Nuts
- Seed and nut butters
Animal protein foods
- Beef
- Pork
- Poultry
- Fish and other seafood
- Eggs
- Wild game
Vary your protein foods.
- Choose plant proteins often.
- Eat seafood twice per week.
- Choose nuts as a snack or salad topping.
- Replace meat or poultry with beans or tofu.
- Try an egg dish as a main course.

Choose protein foods wisely.
- Fish, nuts and seeds contain healthy fat. Choose them often.
- To decrease saturated fat and cholesterol, choose lean cuts of meat such as “loin” or “round.”
- Bake, broil, boil, grill or roast meat and poultry rather than frying.
- Go easy on processed meats as they are high in sodium.
Stretch your food dollar.
- Casseroles and soups help stretch your protein food dollar.
- Try making tacos with lentils or beans.
- Plan two meals with one protein food. For example, bake a whole chicken for one meal and use the leftovers for a casserole or soup.